
Diagnosis of a Stroke
When someone experiences symptoms of a stroke, the most important thing to do is to act B.E.F.A.S.T.
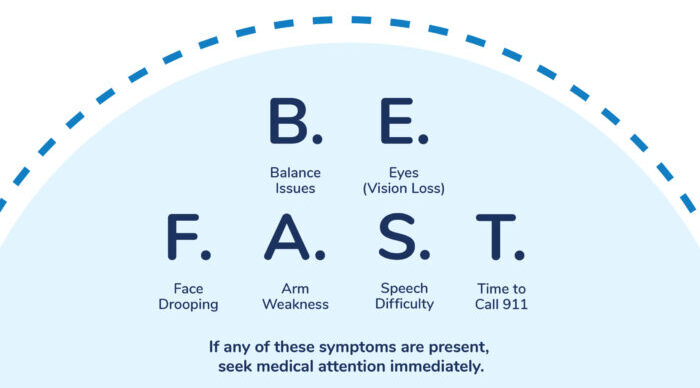
But once you act, how can you know for sure if you’re having a stroke?
Since time is such a crucial factor, patients experiencing a stroke are cared for first in an emergency department at the hospital. As part of providing lifesaving emergency treatment, the medical team will immediately begin to determine the type of stroke by conducting imaging tests using a CT scan or an MRI.
- Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan – A CT scan uses a series of X-rays to create a detailed image of your brain. It can show bleeding in the brain, an ischemic stroke, a tumor, or other conditions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – An MRI uses powerful radio waves and a magnetic field to create a detailed view of the brain. It will show any brain tissue damaged by an ischemic stroke and brain hemorrhages.
To make these imaging tests even more effective, doctors will inject dye into the blood vessels to help highlight any veins and arteries experiencing congestion.
After seeing where the blockage is, your doctor may perform a series of tests to get a complete picture of your overall health and how the stroke may have affected it. These tests may include:
- Physical exam – This comprehensive exam includes listening to the heart, checking blood pressure and conducting a neurological exam to see how a potential stroke has affected the nervous system.
- Blood tests – A series of blood tests to check how fast blood clots, whether the blood sugar is too high or low, whether you have any infections, and other indicators of health problems.
- Carotid ultrasound – Sound waves create detailed images of the inside of the neck’s carotid arteries, highlighting any buildup of fatty deposits called plaque and showing blood flow in the carotid arteries.
- Echocardiogram – Similar to the Carotid ultrasound, this uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart to help find a source of clots that may have traveled from the heart to the brain and caused a stroke.
